Here I write a very simple Python Class. It’s pretty obvious what it does.
# this is an example to illustrate how to # use a class in Python class CAR: #some class variables for this object year = 2016 make = "" model = "" mileage = 0 TotalCar = 0 def __init__(self, year, make, model): self.year = year self.make = make self.model = model CAR.TotalCar += 1 def DisplayCount(self): print ("Total Number of cars %d" % CAR.TotalCar) def displayCar(self): print ("Car Info - MAKE: ", self.make, " , MODEL: ", self.model, " , YEAR: ", self.year, " has total ", self.mileage) #now test the CAR class car_Toyota = CAR(2004, "Toyota", "Camry"); car_Toyota.mileage = 23999 car_HondaCRV = CAR(2015, "Honda", "CR-V"); car_HondaCRV.mileage = 4300 car_Toyota.displayCar() car_HondaCRV.displayCar() print ("Total cars in inventory %d" % CAR.TotalCar) |
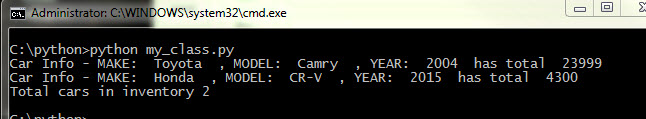
Here’s what the output would look like: